真空泵 |真空泵的種類|真空泵價格
真空泵 |真空泵的種類|真空泵價格
聯繫我們查詢真空泵的價格表和價格
۶۶۷۹۱۷۷۵- (۲۱) ۹۸+
۶۶۷۹۱۷۷۶- (۲۱) ۹۸+
手機:۶۶۱۸۶۷۹- (۹۱۰) ۹۸+
真空泵或真空泵是一種用來產生真空的裝置,用於抽吸氣體。真空泵分為水和油兩大類。產生的低;出口在另一側。)是分開的。本產品的設計需要足夠的經驗和使用優質零件。真空泵的價格是根據類型和功能確定的,無論是新的還是二手的。價格聯繫。
Liánxì wǒmen cháxún zhēnkōngbèng de jiàgé biǎo hé jiàgé.
真空泵或真空泵:
真空泵
循環水(藍環)油性、乾性、動力性
水真空泵多用於重工業,利用水進行冷卻。油泵真空也用於中等工業,使用油冷卻。乾式真空泵也用於輕工業,它的進氣負責冷卻。在更詳細的情況下,我們可以命名旋轉泵、皮帶泵、隔膜泵、噴射泵、離子泵、活塞泵、渦旋泵、托盤泵、滾筒旋轉泵、擴散泵等。
Zhēnkōngbèng huò zhēnkōngbèng:
Zhēnkōngbèng
xúnhuán shuǐ (lán huán) yóuxìng, qiánxìng, dònglì xìng
shuǐ zhēnkōngbèng duōyòng yú zhònggōngyè, lìyòng shuǐ jìnxíng lěngquè. Yóubèng zhēnkōng yě yòng yú zhōngděng gōngyè, shǐyòng yóu lěngquè. Qiánshì zhēnkōngbèng yě yòng yú qīnggōngyè, tā de jìn qì fùzé lěngquè. Zài gèng xiángxì de qíngkuàng xià, wǒmen kěyǐ mìngmíng xuánzhuǎn bèng, pídài bèng, gémó bèng, pēnshè bèng, lízǐ bèng, huósāi bèng, wō xuán bèng, tuōpán bèng, gǔntǒng xuánzhuǎn bèng, kuòsàn bèng děng.
真空技術:
所有過程和物理測量均在低於正常壓力的大氣壓力條件下進行。由於以下原因之一,過程或物理測量通常在真空中進行:
(۱)去除工藝過程中能引起物理或化學反應的大氣成分(如鈦等活性金屬的真空熔煉);
Zhēnkōng jìshù:
Suǒyǒu guòchéng hé wùlǐ cèliáng jūn zài dī yú zhèngcháng yālì de dàqìyā lì tiáojiàn xià jìnxíng. Yóuyú yǐxià yuányīn zhī yī, guòchéng huò wùlǐ cèliáng tōngcháng zài zhēnkōng zhōng jìnxíng:
(۱) Qùchú gōngyì guòchéng zhōng néng yǐnqǐ wùlǐ huò huàxué fǎnyìng de dàqì chéngfèn (rú tài děng huóxìng jīnshǔ de zhēnkōng róngliàn);
۲) 擾亂正常室內條件下存在的平衡狀態,例如去除從大量材料中逸出的阻塞氣體或溶液或液體(例如,脫氣油、除霜)或從表面排出氣體(例如,清潔微波管)和生產過程中的直線加速器)。
(۲) Rǎoluàn zhèngcháng shìnèi tiáojiàn xià cúnzài de pínghéng zhuàngtài, lìrú qùchú cóng dàliàng cáiliào zhōng yì chū de zǔsè qìtǐ huò róngyè huò yètǐ (lìrú, tuō qì yóu, chú shuāng) huò cóng biǎomiàn páichū qìtǐ (lìrú, qīngjié wéibō guǎn) hé shēngchǎn guòchéng zhōng de zhíxiàn jiāsùqì).
(۳) 增加一個粒子在與另一個粒子碰撞之前必須行進的距離,從而幫助粒子在源和目標之間沒有碰撞的情況下移動(例如用於真空鍍膜、粒子加速器、電子管電視圖像);
(۳) Zēngjiā yīgè lìzǐ zài yǔ lìng yīgè lìzǐ pèngzhuàng zhīqián bìxū xíngjìn de jùlí, cóng’ér bāngzhù lìzǐ zài yuán hé mùbiāo zhī jiān méiyǒu pèngzhuàng de qíngkuàng xià yídòng (lìrú yòng yú zhēnkōng dùmó, lìzǐ jiāsùqì, diànzǐguǎn diànshì tú xiàng);
۴) 減少每秒分子效應的數量,從而減少真空中製備的表面受到污染的可能性(在清潔表面研究中很有用)。
對於每個真空過程,可以為最大允許壓力定義一個限制參數。這可以是每單位體積的分子數(原因 ۱ 和 ۲)、平均自由程(原因 ۳)或形成單層所需的時間(原因 ۴)。
۴) Jiǎnshǎo měi miǎo fēnzǐ xiàoyìng de shùliàng, cóng’ér jiǎnshǎo zhēnkōng zhōng zhìbèi de biǎomiàn shòudào wūrǎn de kěnéng xìng (zài qīngjié biǎomiàn yánjiū zhōng hěn yǒuyòng).
Duìyú měi gè zhēnkōng guòchéng, kěyǐ wéi zuìdà yǔnxǔ yālì dìngyì yīgè xiànzhì cānshù. Zhè kěyǐ shì měi dānwèi tǐjī de fēnzǐ shù (yuányīn 1 hé ۲), píngjūn zìyóu chéng (yuányīn 3) huò xíngchéng dān céng suǒ xū de shíjiān (yuányīn 4).
在室溫和自然大氣壓下,۱ 立方英尺(۰٫۰۳ 立方米)的空氣包含大約 ۱۰۲۳,۷۷ 個分子,它們以大約 ۱۰۰۰ 英里/小時(۱۶۰۰ 公里/小時)的速度沿隨機方向行進。牆壁的匯率是每平方英寸牆壁表面 ۷ ۱۴٫۷。這種大氣壓可以用多種單位表示,但直到最近,它通常以汞柱的重量、截面積和 ۷۶۰ 毫米的高度來表示。
Zài shì wēnhé zìrán dàqìyā xià,۱ lìfāng yīngchǐ (۰٫۰۳ Lìfāng mǐ) de kōngqì bāohán dàyuē ۱۰۲۳,۷۷ gè fēnzǐ, tāmen yǐ dàyuē ۱۰۰۰ yīnglǐ/xiǎoshí (۱۶۰۰ gōnglǐ/xiǎoshí) de sùdù yán suíjī fāngxiàng xíngjìn. Qiángbì de huìlǜ shì měi píngfāng yīngcùn qiángbì biǎomiàn 7 14.7. Zhè zhǒng dàqìyā kěyǐ yòng duōzhǒng dānwèi biǎoshì, dàn zhídào zuìjìn, tā tōngcháng yǐ gǒng zhù de zhòngliàng, jié miànjī hé ۷۶۰ háomǐ de gāodù lái biǎoshì.因此,標準大氣等效於 ۷۶۰ 毫米汞柱,但假定術語 torr 以避免均衡看似不同的單位的異常。一個標準大氣壓 = ۷۶۰ 托(۱ 托 = ۱ 毫米汞柱)。 ۱۹۷۱ 年,該術語被定義為每平方米牛頓 (N / m2) 的 SI 單位所取代,稱為帕斯卡(一帕斯卡 = ۷٫۵ ۷٫ ۱۰-۳ 托)。
Yīncǐ, biāozhǔn dàqì děng xiào yú ۷۶۰ háomǐ gǒng zhù, dàn jiǎdìng shùyǔ torr yǐ bìmiǎn jūnhéng kàn shì bùtóng de dānwèi de yìcháng. Yīgè biāozhǔn dàqìyā = ۷۶۰ tuō (۱ tuō = ۱ háomǐ gǒng zhù). ۱۹۷۱ Nián, gāi shùyǔ bèi dìngyì wèi měi píngfāng mǐ niúdùn (N/ m2) de SI dānwèi suǒ qǔdài, chēng wèi pàsīkǎ (yī pàsīkǎ = ۷٫۵ ۷٫ ۱۰-۳ Tuō).
真空技術在工業中的第一次主要應用發生在 ۱۹۰۰ 年左右的燈泡生產中。其他需要真空才能工作的設備,例如不同類型的電子管。此外,還發現一些過程是在真空中進行的,或者取得了非凡的結果,或者在正常天氣條件下是無法實現的。此類改進包括“開花”鏡片表面以增加透光率、為血庫製備血漿以及生產鈦等活性金屬。 ۱۹۵۰ 年代核電的出現為大型真空設備的發展提供了動力。越來越多的真空過程應用,如空間模擬和微電子,正在穩步被發現。
Zhēnkōng jìshù zài gōngyè zhōng de dì yī cì zhǔyào yìngyòng fāshēng zài 1900 nián zuǒyòu de dēngpào shēngchǎn zhōng. Qítā xūyào zhēnkōng cáinéng gōngzuò de shèbèi, lìrú bùtóng lèixíng de diànzǐguǎn. Cǐwài, hái fāxiàn yīxiē guòchéng shì zài zhēnkōng zhōng jìnxíng de, huòzhě qǔdéle fēifán de jiéguǒ, huòzhě zài zhèngcháng tiānqì tiáojiàn xià shì wúfǎ shíxiàn de. Cǐ lèi gǎijìn bāokuò “kāihuā” jìngpiàn biǎomiàn yǐ zēngjiā tòu guāng lǜ, wèi xuèkù zhìbèi xiějiāng yǐjí shēngchǎn tài děng huóxìng jīnshǔ. ۱۹۵۰ Niándài hédiàn de chūxiàn wéi dàxíng zhēnkōng shèbèi de fāzhǎn tígōngle dònglì. Yuè lái yuè duō de zhēnkōng guòchéng yìngyòng, rú kōngjiān mónǐ hé wéi diànzǐ, zhèngzài wěnbù pī fà xiàn.
已經開發了各種類型的設備用於真空的產生、維護和測量。下面描述了一些重要的類型。
真空泵的種類
在劃分了主要類別之後,我們將處理每個類別的子集:第一類的子集是:
一步藍真空
二級藍色真空
液環氣體壓縮機
第二類子集是:
一步油真空
兩級油真空
第三類子集是:
旋轉式
隔膜
活塞
助推器
???
側通道
擰緊
滾動
Yǐjīng kāifāle gèzhǒnglèixíng de shèbèi yòng yú zhēnkōng de chǎnshēng, wéihù hé cèliáng. Xiàmiàn miáoshùle yīxiē zhòngyào de lèixíng.
Zhēnkōngbèng de zhǒng lèi
zài huàfēnle zhǔyào lèibié zhīhòu, wǒmen jiāng chǔlǐ měi gè lèibié de zǐ jí: Dì yī lèi de zǐ jí shì:
Yībù lán zhēnkōng
èr jí lán sè zhēnkōng
yè huán qìtǐ yāsuō jī
dì èr lèi zǐ jí shì:
Yībù yóu zhēnkōng
liǎng jí yóu zhēnkōng
dì sān lèi zǐ jí shì:
Xuánzhuǎn shì
gémó
huósāi
zhù tuī qì
???
cè tōngdào
níngjǐn
gǔndòng
第四類的子類是:
噴射器
擴散
分子渦輪
離子泵
旋轉葉片在泵中的工作原理: ۱٫ 膨脹階段(入口打開和低壓)(內毒素) ۲٫ 隔離(入口關閉)(分解) ۳٫ 高壓壓縮階段(壓縮) ۴٫ 外部變成氣體
一般來說,這些泵在健康、壓力、使用壽命、對流體和化學品的耐受性以及質量等因素方面存在差異。
閱讀這篇文章對你也很有用!潤滑脂和真空油
Dì sì lèi de zi lèi shì:
Pēnshè qì
kuòsàn
fēnzǐ wōlún
lízǐ bèng
xuánzhuǎn yèpiàn zài bèng zhōng de gōngzuò yuánlǐ: ۱٫ Péngzhàng jiēduàn (rùkǒu dǎkāi hé dīyā)(nèi dúsù) ۲٫ Gélí (rùkǒu guānbì)(fēnjiě) ۳٫ Gāoyā yāsuō jiēduàn (yāsuō) ۴٫ Wàibù biànchéng qìtǐ
yībān lái shuō, zhèxiē bèng zài jiànkāng, yālì, shǐyòng shòumìng, duì liútǐ hé huàxué pǐn de nài shòu xìng yǐjí zhìliàng děng yīnsù fāngmiàn cúnzài chāyì.
Yuèdú zhè piān wénzhāng duì nǐ yě hěn yǒuyòng! Rùnhuá zhī hé zhēnkōng yóu 真空泵的使用方法及安全:
這些組件很堅固並且有潛在危險。潛在風險包括:
受污染的泵油進入泵
意外接觸運動部件造成的損壞
接線故障引起的電擊
因過熱或其他缺陷引起的火災
由於通風不當而產生的有毒煙霧
安全應該始終是您的首要任務。關鍵的健康和安全考慮包括:
Zhēnkōngbèng de shǐyòng fāngfǎ jí ānquán:
Zhèxiē zǔjiàn hěn jiāngù bìngqiě yǒu qiánzài wéixiǎn. Qiánzài fēngxiǎn bāokuò:
Shòu wūrǎn de bèng yóu jìnrù bèng
yìwài jiēchù yùndòng bùjiàn zàochéng de sǔnhuài
jiēxiàn gùzhàng yǐnqǐ de diànjí
yīn guòrè huò qítā quēxiàn yǐnqǐ de huǒzāi
yóuyú tōngfēng bùdāng ér chǎnshēng de yǒudú yānwù
ānquán yīnggāi shǐzhōng shì nín de shǒuyào rènwù. Guānjiàn de jiànkāng hé ānquán kǎolǜ bāokuò:
術前了解自己
監控油位並準備好在必要時換油
正確丟棄任何油
切勿堵塞或堵塞排氣或泵出口
使用正確的 PPE
不要在密閉或不通風的區域操作泵
如果可能,請使用通風櫃
確保皮帶防護裝置就位
發生錯誤時,使用漏液盤防止漏液
確保管道與泵完全兼容並適合使用 – 必要時更換
檢查可燃材料的環境
檢查開關和電纜是否存在可能的故障
Shù qián liǎojiě zìjǐ
jiānkòng yóu wèi bìng zhǔnbèi hǎo zài bìyào shí huàn yóu
zhèngquè diūqì rènhé yóu
qiè wù dǔsè huò dǔsè pái qì huò bèng chūkǒu
shǐyòng zhèngquè de PPE
bùyào zài mìbì huò bù tōngfēng de qūyù cāozuò bèng
rúguǒ kěnéng, qǐng shǐyòng tōngfēng guì
quèbǎo pídài fánghù zhuāngzhì jiù wèi
fāshēng cuòwù shí, shǐyòng lòu yè pán fángzhǐ lòu yè
quèbǎo guǎndào yǔ bèng wánquán jiānróng bìng shìhé shǐyòng – bìyào shí gēnghuàn
jiǎnchá kěrán cáiliào de huánjìng
jiǎnchá kāiguān hé diànlǎn shìfǒu cúnzài kěnéng de gùzhàng
您還應該考慮實用技巧:
泵尺寸
該計劃旨在
泵型
實施要求
常見問題(泵的應用):
*) 水泵和油泵的基本部件是什麼?
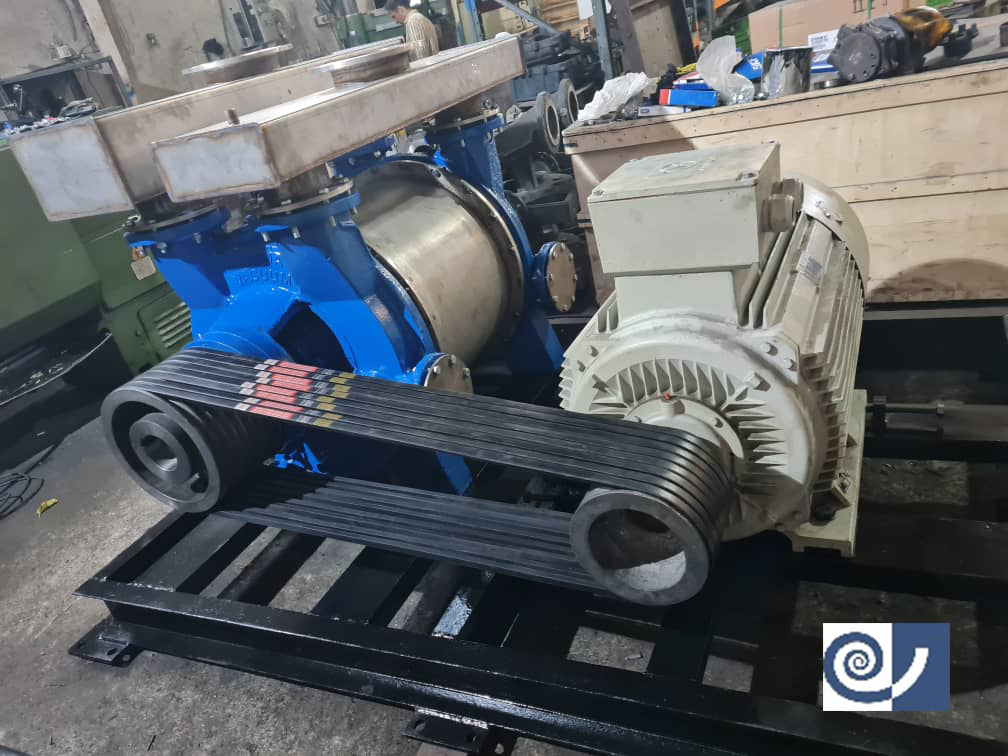
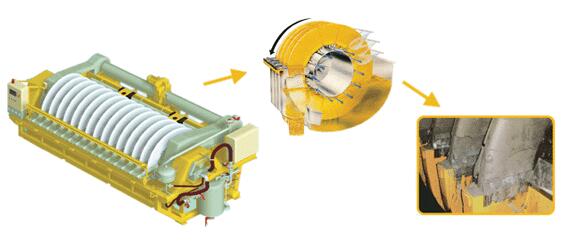
此類真空泵的主要部件有密封碗、分離器過濾器、軸、機櫃、電動泵、轉子、泵體、軟管和……。
Nín hái yīnggāi kǎolǜ shíyòng jìqiǎo:
Bèng chǐcùn
gāi jìhuà zhǐ zài
bèng xíng
shíshī yāoqiú
chángjiàn wèntí (bèng de yìngyòng):
*) Shuǐbèng hé yóubèng de jīběn bùjiàn shì shénme?
Cǐ lèi zhēnkōngbèng de zhǔyào bùjiàn yǒu mìfēng wǎn, fēnlí qì guòlǜ qì, zhóu, jīguì, diàndòng bèng, zhuànzǐ, bèng tǐ, ruǎn guǎn hé…….
*) 藍色真空和油真空適用於哪些公司和組織?
這些類型的泵廣泛用於研究和實驗室公司、大型工廠和生產、軍事組織、醫院、大學。例如,在藥房和實驗室,在水泥、造紙、玻璃、木材工業、金屬廠、食品工業和……等工廠。
*) 水真空和油真空可以用在什麼地方或位置?
我們在我們的專家和專家顧問的指導下,根據從客戶那裡收到的信息來有效地設置或修改您的系統。
閱讀這篇文章對你也很有用!真空泵維修和備件
*) Lán sè zhēnkōng hé yóu zhēnkōng shìyòng yú nǎxiē gōngsī hé zǔzhī?
Zhèxiē lèixíng de bèng guǎngfàn yòng yú yánjiū hé shíyàn shì gōngsī, dàxíng gōngchǎng hé shēngchǎn, jūnshì zǔzhī, yīyuàn, dàxué. Lìrú, zài yàofáng hé shíyàn shì, zài shuǐní, zàozhǐ, bōlí, mùcái gōngyè, jīnshǔ chǎng, shípǐn gōngyè hé……děng gōngchǎng.
*) Shuǐ zhēnkōng hé yóu zhēnkōng kěyǐ yòng zài shénme dìfāng huò wèizhì?
Wǒmen zài wǒmen de zhuānjiā hé zhuānjiā gùwèn de zhǐdǎo xià, gēnjù cóng kèhù nàlǐ shōu dào de xìnxī lái yǒuxiào dì shèzhì huò xiūgǎi nín de xìtǒng.
Yuèdú zhè piān wénzhāng duì nǐ yě hěn yǒuyòng! Zhēnkōngbèng wéixiū hé bèi jiàn
*) 我們如何創造真空?
真空泵在上下兩個空間中產生不同水平的壓力。當這些區域相連時,空氣分子從高壓空間被吸入低壓空間,第一個空間是空的。換句話說,它創造了一個真空。
也可以使用根據投資原理運行的真空發生器產生真空。這是壓縮空氣通過一個危險室的地方,該室旨在將氣體或液體輸送出該區域。文丘里管或噴射流體發生器依靠壓縮空氣、氣體或液體流作為驅動流體在相關端口中抽吸或產生真空。
真空泵出現故障怎麼辦?
*) Wǒmen rúhé chuàngzào zhēnkōng?
Zhēnkōngbèng zài shàngxià liǎng gè kōngjiān zhōng chǎnshēng bùtóng shuǐpíng de yālì. Dāng zhèxiē qūyù xiānglián shí, kōngqì fēnzǐ cóng gāoyā kōngjiān bèi xīrù dīyā kōngjiān, dì yīgè kōngjiān shì kōng de. Huàn jù huàshuō, tā chuàngzàole yīgè zhēnkōng.
Yě kěyǐ shǐyòng gēnjù tóuzī yuánlǐ yùnxíng de zhēnkōng fāshēng qì chǎnshēng zhēnkōng. Zhè shì yāsuō kōngqì tōngguò yī gè wéixiǎn shì dì dìfāng, gāi shì zhǐ zài jiāng qìtǐ huò yètǐ shūsòng chū gāi qūyù. Wénqiū lǐ guǎn huò pēnshè liútǐ fāshēng qì yīkào yāsuō kōngqì, qìtǐ huò yètǐ liú zuòwéi qūdòng liútǐ zài xiāngguān duānkǒu zhōng chōu xī huò chǎnshēng zhēnkōng.
Zhēnkōngbèng chūxiàn gùzhàng zěnme bàn?
像所有機械設備一樣,真空泵偶爾會出現故障。可能是突然故障,例如某天水泵拒絕開啟,但由於內部問題隨著時間的推移而惡化,您更有可能經歷症狀的逐漸積累。
即將發生故障的常見跡象包括:
漏油
嘈雜的操作
抽煙
真空壓降
*) 什麼是真空裝置?
Xiàng suǒyǒu jīxiè shèbèi yīyàng, zhēnkōngbèng ǒu’ěr huì chūxiàn gùzhàng. Kěnéng shì túrán gùzhàng, lìrú mǒu tiān shuǐbèng jùjué kāiqǐ, dàn yóuyú nèibù wèntí suízhe shíjiān de tuīyí ér èhuà, nín gèng yǒu kěnéng jīnglì zhèngzhuàng de zhújiàn jīlěi.
Jíjiāng fāshēng gùzhàng de chángjiàn jīxiàng bāokuò:
Lòu yóu
cáozá de cāozuò
chōuyān
zhēnkōng yā jiàng
*) shénme shì zhēnkōng zhuāngzhì?
帕斯卡(Pa)是以法國物理學家布萊斯·帕斯卡命名的國際標準壓力單位。它有時用於測量真空,但更常見的單位是托,這個術語來自不同的物理學家——意大利人 Evangelista Torricelli。
Torr 相當於標準大氣壓的 ۱/۷۶۰。直到最近,還使用了不同的定義——相當於每壓力計毫米汞柱。
*) 真空泵和壓縮機有什麼區別?
Pàsīkǎ (Pa) shì yǐ fàguó wùlǐ xué jiā bù lái sī·pàsīkǎ mìngmíng de guójì biāozhǔn yālì dānwèi. Tā yǒu shí yòng yú cèliáng zhēnkōng, dàn gèng chángjiàn de dānwèi shì tuō, zhège shùyǔ láizì bùtóng de wùlǐ xué jiā——yìdàlì rén Evangelista Torricelli.
Torr xiāngdāng yú biāozhǔn dàqìyā de 1/760. Zhídào zuìjìn, hái shǐ yòng liǎo bùtóng de dìngyì——xiāngdāng yú měi yālì jì háomǐ gǒng zhù.
*) Zhēnkōngbèng hé yāsuō jī yǒu shé me qūbié?
這兩種設備有不同的目標。這些泵旨在通過高壓區和低壓區的組合產生真空。相比之下,壓縮機將空氣從周圍環境中抽出並用高壓壓縮。這為氣動工具和設備的最終放電節省了能源。
*) 真空泵的用途是什麼?
真空泵用於從密封體積中去除空氣或氣體分子,從而產生真空。例如,真空度可以通過特定壓力下的工藝氣體來控制。
*) 什麼是真空泵,它是如何工作的?
Zhè liǎng zhǒng shèbèi yǒu bùtóng de mùbiāo. Zhèxiē bèng zhǐ zài tōngguò gāoyā qū hé dīyā qū de zǔhé chǎnshēng zhēnkōng. Xiāng bǐ zhī xià, yāsuō jī jiāng kōngqì cóng zhōuwéi huánjìng zhōng chōuchū bìngyòng gāoyā yāsuō. Zhè wéi qìdòng gōngjù hé shèbèi de zuìzhōng fàngdiàn jiéshěngle néngyuán.
*) Zhēnkōngbèng de yòngtú shì shénme?
Zhēnkōngbèng yòng yú cóng mìfēng tǐjī zhōng qùchú kōngqì huò qìtǐ fēnzǐ, cóng’ér chǎnshēng zhēnkōng. Lìrú, zhēnkōng dù kěyǐ tōngguò tèdìng yālì xià de gōngyì qìtǐ lái kòngzhì.
*) Shénme shì zhēnkōngbèng, tā shì rúhé gōngzuò de?
真空泵基本上是通過改變高壓和低壓狀態將氣體分子從一個區域移動到另一個區域以產生真空。通過從真空空間去除分子,去除多餘的分子變得更加困難,從而增加了所需的真空功率。
*) 我應該在真空泵中尋找什麼?
還要考慮以下可能影響真空泵選擇的特性:
化學相容性。
抽速(體積流量)和所需壓力。
安裝泵。
泵維護。
費用
Zhēnkōngbèng jīběn shàng shì tōngguò gǎibiàn gāoyā hé dīyā zhuàngtài jiāng qìtǐ fēnzǐ cóng yīgè qūyù yídòng dào lìng yīgè qūyù yǐ chǎnshēng zhēnkōng. Tōngguò cóng zhēnkōng kōngjiān qùchú fēnzǐ, qùchú duōyú de fēnzǐ biàn dé gèngjiā kùnnán, cóng’ér zēngjiāle suǒ xū de zhēnkōng gōnglǜ.
*) Wǒ yīnggāi zài zhēnkōngbèng zhōng xúnzhǎo shénme?
Hái yào kǎolǜ yǐxià kěnéng yǐngxiǎng zhēnkōngbèng xuǎnzé de tèxìng:
Huàxué xiāng róng xìng.
Chōu sù (tǐjī liúliàng) hé suǒ xū yālì.
Ānzhuāng bèng.
Bèng wéihù.
Fèiyòng
*) 兩種常見的真空泵類型是什麼?
真空泵有兩大類:氣體輸送泵和捕集或抽吸泵
*) 真空的例子是什麼?
任何壓力低於大氣壓的區域都是真空。 … 真空吸塵器的吸力會產生真空。保溫瓶玻璃壁之間的保溫區是真空的。地球的熱層是真空。強低風暴壓力是局部真空。
*) 我們需要多少真空泵?
*) Liǎng zhǒng chángjiàn de zhēnkōngbèng lèixíng shì shénme?
Zhēnkōngbèng yǒu liǎng dàlèi: Qìtǐ shūsòng bèng hé bǔ jí huò chōu xī bèng
*) zhēnkōng de lìzi shì shénme?
Rènhé yālì dī yú dàqìyā de qūyù dōu shì zhēnkōng. … Zhēnkōng xīchénqì de xīlì huì chǎnshēng zhēnkōng. Bǎowēn píng bōlí bì zhī jiān de bǎowēn qū shì zhēnkōng de. Dìqiú de rè céng shì zhēnkōng. Qiáng dī fēngbào yālì shì júbù zhēnkōng.
*) Wǒmen xūyào duōshǎo zhēnkōngbèng?
決定空調製冷泵最實用的方法是得到您使用的噸位的平方根。 … ۱۶ 噸到 ۲۵ 噸(典型的住宅空調系統)需要 CFM 等級為 ۴ 到 ۵ 的泵。 ۱۶ 到 ۲۵ 噸(商業系統)需要 ۶ 到 ۸ CFM 的額定值。
*) 什麼是最好的真空泵?
德國 leybold – 德國博世 – 德國 CIHI – 意大利 Robuschi
shimatsu Japan – Woosung South Korea – Vacuum Pars – Asia Vacuum
*) 真空泵有哪些類型?
Juédìng kòngtiáo zhìlěng bèng zuì shíyòng de fāngfǎ shì dédào nín shǐyòng de dùnwèi de píngfānggēn. … 16 Dūn dào 25 dūn (diǎnxíng de zhùzhái kòngtiáo xìtǒng) xūyào CFM děngjí wèi 4 dào 5 de bèng. 16 Dào 25 dūn (shāngyè xìtǒng) xūyào 6 dào 8 CFM de é dìng zhí.
*) Shénme shì zuì hǎo de zhēnkōngbèng?
Déguó leybold – déguó bóshì – déguó CIHI – yìdàlì Robuschi
shimatsu Japan – Woosung South Korea – Vacuum Pars – Asia Vacuum
*) zhēnkōngbèng yǒu nǎxiē lèixíng?
這些真空範圍的不同類型的泵可分為初級(備用)泵、增壓泵和次級泵(高真空):真空壓力範圍、非常高和極高。真空泵主要有兩大類:氣體輸送泵和捕集泵
*) 為什麼真空泵需要油?
真空泵油在真空泵的運行中是必不可少的。這台機器潤滑泵,同時從排放的系統中收集污染物和水分。 … 這些使用的油必須是純添加劑(抗氧化、抗泡或抗腐蝕添加劑除外)
*) 真空泵是如何分類的?
Zhèxiē zhēnkōng fànwéi de bùtóng lèixíng de bèng kě fēn wéi chūjí (bèiyòng) bèng, zēng yā bèng hé cì jí bèng (gāo zhēnkōng): Zhēnkōng yālì fànwéi, fēicháng gāo hè jí gāo. Zhēnkōngbèng zhǔyào yǒu liǎng dàlèi: Qìtǐ shūsòng bèng hé bǔ jí bèng
*) wèishéme zhēnkōngbèng xūyào yóu?
Zhēnkōngbèng yóu zài zhēnkōngbèng de yùnxíng zhōng shì bì bùkě shǎo de. Zhè tái jīqì rùnhuá bèng, tóngshí cóng páifàng de xìtǒng zhōng shōují wūrǎn wù hé shuǐfèn. … Zhèxiē shǐyòng de yóu bìxū shì chún tiānjiājì (kàng yǎnghuà, kàng pào huò kàng fǔshí tiānjiājì chúwài)
*) zhēnkōngbèng shì rúhé fēnlèi de?
真空泵分為氣體輸送泵和氣體連接泵或接收泵。 … 輸氣泵,也稱為輸氣泵,分為正排量泵或動力真空泵。
*) 真空泵位於何處?
大多數真空泵位於發動機的左側或右側,在柴油車中通常更靠近主制動缸。真空泵由於頻繁使用,需要油來保持適當的潤滑和降低內部溫度。
*) 如何在離心泵中產生真空?
Zhēnkōngbèng fēn wéi qìtǐ shūsòng bèng hé qìtǐ liánjiē bèng huò jiēshōu bèng. … Shū qì bèng, yě chēng wèi shū qì bèng, fēn wéi zhèng pái liàng bèng huò dònglì zhēnkōngbèng.
*) Zhēnkōngbèng wèiyú hé chù?
Dà duōshù zhēnkōngbèng wèiyú fādòngjī de zuǒcè huò yòucè, zài cháiyóu chē zhōng tōngcháng gèng kàojìn zhǔ zhìdòng gāng. Zhēnkōngbèng yóuyú pínfán shǐyòng, xūyào yóu lái bǎochí shìdàng de rùnhuá hé jiàngdī nèibù wēndù.
*) Rúhé zài líxīn bèng zhōng chǎnshēng zhēnkōng?
離心泵使用離心力移動液體以產生流體速度。流體通過吸嘴進入泵。葉輪葉片捕獲流體並沿切向和徑向旋轉,從排放側排出泵。
*) 如果真空泵中殘留臟油會怎樣?
受污染的油會堵塞油霧過濾器,增加泵內的工作壓力並最終使發動機過載(並且在嚴重污染的情況下可能會撕裂油過濾器)。用於復合材料行業的真空泵通過來自電機風扇的氣流冷卻
*) 為什麼真空泵會冒煙?
Líxīn bèng shǐyòng líxīnlì yídòng yètǐ yǐ chǎnshēng liútǐ sùdù. Liútǐ tōngguò xī zuǐ jìnrù bèng. Yèlún yèpiàn bǔhuò liútǐ bìng yán qiè xiàng hé jìng xiàng xuánzhuǎn, cóng páifàng cè páichū bèng.
*) Rúguǒ zhēnkōngbèng zhōng cánliú zàng yóu huì zěnyàng?
Shòu wūrǎn de yóu huì dǔsè yóu wù guòlǜ qì, zēngjiā bèng nèi de gōngzuò yālì bìng zuìzhōng shǐ fādòngjī guòzǎi (bìngqiě zài yánzhòng wūrǎn de qíngkuàng xià kěnéng huì sī liè yóu guòlǜ qì). Yòng yú fùhé cáiliào hángyè de zhēnkōngbèng tōngguò láizì diànjī fēngshàn de qìliú lěngquè
*) wèishéme zhēnkōngbèng huì mào yān?
他們不抽煙。這是一個機械蒸汽油泵。泵在抽水時有蒸汽進入腔室是正常的。因為由泵腔離開腔室的所有空氣都經過油箱中的油,所以當大量空氣通過時,其中一部分會蒸發。
*) 我可以在真空泵中使用發動機油嗎?
切勿將發動機/發動機油用於您的旋轉真空泵。 … 發動機油的粘度與真空泵油不同,完全沒有真空特性。發動機油含有多種添加劑,如防銹劑和防腐蝕化合物
Tāmen bù chōuyān. Zhè shì yīgè jīxiè zhēngqì yóubèng. Bèng zài chōushuǐ shí yǒu zhēngqì jìnrù qiāng shì shì zhèngcháng de. Yīnwèi yóu bèng qiāng líkāi qiāng shì de suǒyǒu kòng qì dōu jīngguò yóuxiāng zhōng de yóu, suǒyǐ dāng dàliàng kōngqì tōngguò shí, qízhōng yībùfèn huì zhēngfā.
*) Wǒ kěyǐ zài zhēnkōngbèng zhōng shǐyòng fādòngjī yóu ma?
Qiè wù jiāng fādòngjī/fādòngjī yóu yòng yú nín de xuánzhuǎn zhēnkōngbèng. … Fādòngjī yóu de niándù yǔ zhēnkōngbèng yóu bùtóng, wánquán méiyǒu zhēnkōng tèxìng. Fādòngjī yóu hányǒu duōzhǒng tiānjiājì, rú fáng xiù jì hé fáng fǔshí huàhéwù
*) 如何將真空變成水泵?
一些 Shop Vac 具有“水泵”功能。您可以將花園軟管連接到空白空間的側端口,而不僅僅是將水倒入罐中,它實際上將水泵送到另一個位置。如果你沒有這樣的空間,你可以喝水直到罐裝滿。
*) 什麼是濕式真空泵?
濕式真空泵基本上是泵送空氣而不是液體的液壓泵。泵葉片由發動機油潤滑。濕泵使用壽命長。由於內部組件是用油潤滑的(因此稱為“濕式”泵),因此內部組件比干式泵更耐磨損。
真空泵品牌:
*) Rúhé jiāng zhēnkōng biànchéng shuǐbèng?
Yīxiē Shop Vac jùyǒu “shuǐbèng” gōngnéng. Nín kěyǐ jiāng huāyuán ruǎn guǎn liánjiē dào kòngbái kōngjiān de cè duānkǒu, ér bùjǐn jǐn shì jiāng shuǐ dào rù guàn zhōng, tā shíjì shang jiāng shuǐbèng sòng dào lìng yīgè wèizhì. Rúguǒ nǐ méiyǒu zhèyàng de kōngjiān, nǐ kěyǐ hē shuǐ zhídào guàn zhuāng mǎn.
*) Shénme shì shī shì zhēnkōngbèng?
Shī shì zhēnkōngbèng jīběn shàng shì bèng sòng kōngqì ér bùshì yètǐ de yèyā bèng. Bèng yèpiàn yóu fādòngjī yóu rùnhuá. Shī bèng shǐyòng shòumìng zhǎng. Yóuyú nèibù zǔjiàn shì yòng yóu rùnhuá de (yīncǐ chēng wèi “shī shì” bèng), yīncǐ nèibù zǔjiàn bǐ gàn shì bèng gèng nài mó sǔn.
Zhēnkōngbèng pǐnpái: